Healthcare is a very data-driven industry. Healthcare organizations depend on reliable, efficient access to patient records in order to make diagnoses and provide high-quality care. SD and microSD memory cards are employed in a number of medical uses for hospitals and medical devices.
According to World Economic Forum, hospitals produce 50 petabytes of data per year. This mountain of data is comprised of information from sensors and monitoring equipment, clinician notes, lab tests, medications and other operational data. Various sources of medical imaging including MRI, PET/CT scans, ultrasounds, x-rays and more are also part of the mix. The ability to collect, store and use medical data has helped establish new levels of efficiency and accuracy in healthcare, but medicine is moving beyond the walls of hospitals, and manufacturers today are relying on SD memory cards for medical devices to fuel a revolution of care.
A key motivator behind the implementation of SD and microSD memory cards is the demand for mobility in healthcare applications. Storage solutions need to be highly reliable, have low power requirements, and be lightweight and small enough to be easily integrated into a wide spectrum of medical equipment without concerns over storage space.
SD memory cards provide a proven platform for medical devices designed for demanding conditions. The cards deliver fast data transfer rates and defined recording speeds that are crucial in lifesaving situations. They are also easy to clean and sanitize.
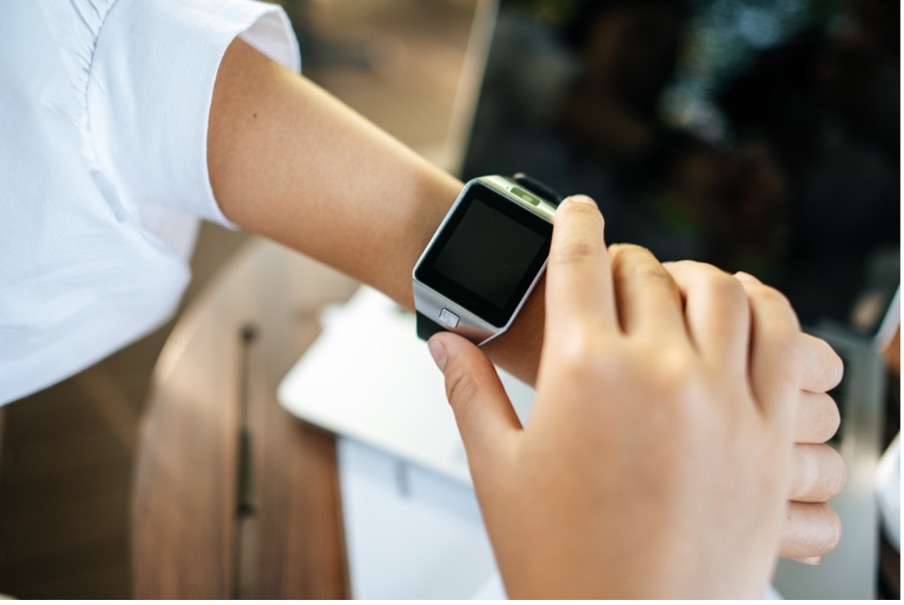

Wearables
SD memory cards are often employed in the creation of wearable medical devices, including mobile health or mHealth applications. An example is wrist-worn devices, that are more common because they are a convenient and familiar form factor. These devices easily place sensors in constant contact with the skin and track vital signs, heart rate monitors and pacemakers. SD memory cards help to keep patient-generated data secure while allowing them to be transferred quickly during consultation or diagnosis. SD memory cards are also embedded into smart watches, activity bands and other monitors.
Telemedicine
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the need for remote, telemedicine services since in-person health services was restricted due to the risk of infections and limited health resources. For this reason, telemedicine services have proved extremely useful by providing home monitoring and rehabilitation solutions, helping reduce the risk of infection.
SD memory cards are used in devices for monitoring physical activity and movement in sports rehabilitation. In this case, it is helpful to measure, analyze and evaluate physiological parameters involving a patient’s actions. An example is a knee brace with numerous sensors and microphones to monitor knee joint health. Similar devices also support both diagnosis and ongoing treatment for many diseases involving movement disorders. Furthermore, home-based motion sensing could assist with rehabilitation and falls prevention, helping improve independence and lifestyle. Sensors and data storage are now essential in the tele-rehabilitation path to obtain and store accurate and reliable information to analyze physiological signals.
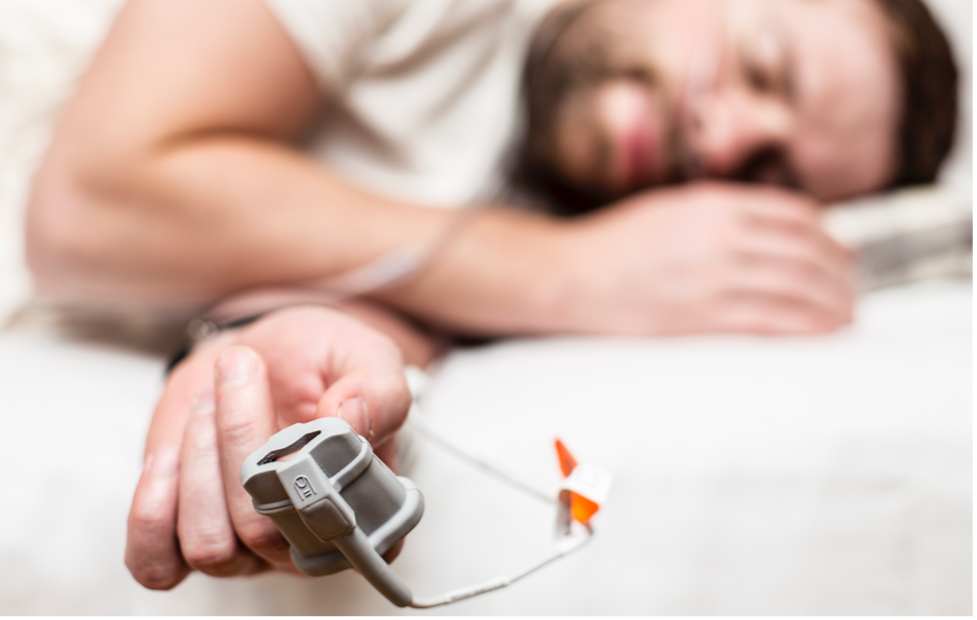
Monitoring offline
When a patient’s vital signs need monitoring over a long period of time during the patient’s normal daily life, offline medical devices collect data in the background. The data is be stored in real-time on microSD memory cards then reviewed by medical professionals for diagnosis and prediction. One example is tracking a patient with sleep apnea. A home sleep monitoring device allows the patient to sleep in a familiar environment with reliable data acquisition as opposed to requiring the patient to sleep at a facility for tracking.

Preparing for the next generation of medical devices
A challenge facing the industry is that the next generation of high-performance medical devices will collect even more massive amounts of data at even faster rates, while requiring the same portability and small form factors. In other words, the obstacle will be to efficiently store all of that data used by data-hungry applications. In such cases, SD memory cards provide an effective solution. SD Express memory cards leverage the PCI Express® and NVM Express® architectures, alongside legacy SD interface. The SD 8.0 and SD 7.x specifications for SD Express cards allow for transfer speeds of up to 4 GB/s and up to 985MB/s respectively– representing a significant jump from the legacy SD UHSII and SD UHS-I cards supporting up to 312MB/s and 104MB/s respectively. These innovative and advanced technologies open even more possibilities and opportunities for SD memory cards and applications in the future.
Hiroyuki Sakamoto is president of the SD Association. He can be reached at president@sdcard.org.
SD trademarks are owned and licensed by SD-3C LLC.
PCI Express® and PCIe® registered trademarks of PCI-SIG®.
NVM Express™ and NVMe™ are trademarks of NVM Express, Inc.
©2022 SD Association. All Rights Reserved.




