An Introduction to SD Standards
SD standards enable manufacturers to deliver high-performance products that enhance the experience of millions of people every day who listen to music, record videos, take photos, save data and use a mobile phone.
As the industry standard, the SD standard is utilized across multiple market segments of the portable storage industry,including mobile phones, digital cameras, MP3 players, personal computers, tablets, printers, car navigation systems,electronic books, and many other consumer electronic devices.
There are three defined form factors for SD memory cards; full size, miniSD and microSD. microSD took replaced miniSD, therefore, two form factors are more commonly found in the marketplace and are shown in table below.
Conventional SD memory cards only have one row of pins including a 3.3V power supply VDD that are used for Default Speed,High Speed and UHS-I bus interface modes. Full size cards have 9 pins (two VSS) and microSD cards have 8 pins (one VSS).
Faster bus transfer speed cards have a new pin layout on the second-row to support UHS-IIand SD Express transfer speeds. 1.8V VDD is included in the second-row pins. All UHS-II and SD Express cards require two power supply voltages 3.3V and 1.8V and optional 1.2v supply for microSD Express cards. Note that the SD specification includes also a higher speed of UHS version named UHS-III, not covered here, but can be found in the SDA members website.
Non UHS-II microSD Card may extend two antenna pads for contactless applications but antenna pads will interfere the second row of UHS-II Cards. NFC (Near Field Communication) Interface was defined alternatively that use Single Wire Protocol via a pad on the second row.
| Form Factor | SD | microSD | |
| Dimension | 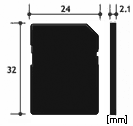 |
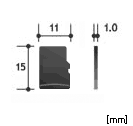 |
|
| Card Capacity Type | SD, SDHC, SDXC and SDUC | ||
| Physical | Number of pins |
High Speed and UHS-I : 9 pins UHS-II: 17 pins SD Express 1-lane: 17-19 pins SD Express 2-lane: 25-27 pins |
High Speed and UHS-I : 8 pins UHS-II: 16 pins SD Express 1-lane: 16-17 pins |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V VDD range in the first-row: 2.7V – 3.6V 1.8V VDD range in the second-row: 1.70V-1.95V |
||
| Write-protect Switch | YES | NO | |
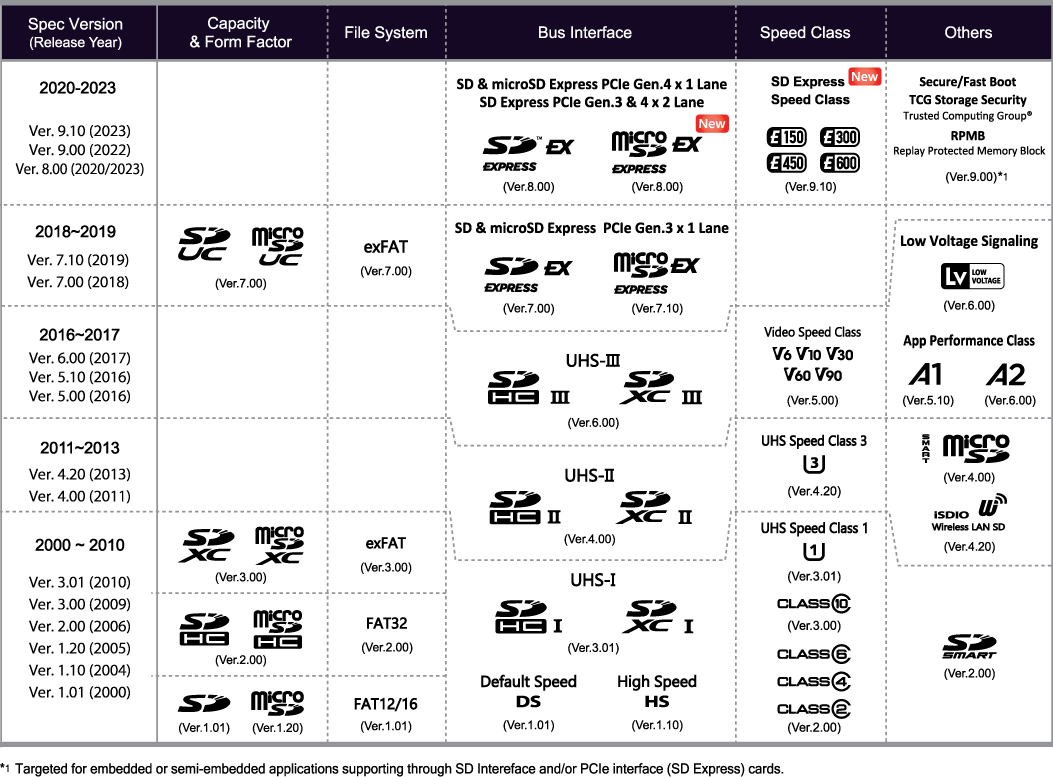
NAND technology showed amazing progress that provided exponential memory capacity increase. Much faster bus interface speed is required in accordance with increase of memory capacity to shorten access time to such capacity card.
UHS-II offer much higher bus speeds than UHS-I using Low Voltage Differential Signal (LVDS) found on the second-row pins. The new SD Express speed are the fastest. The first-row of pins on UHS-II and SD Express cards provide
backward compatibility and interoperability with conventional interface host devices.
SD Standard Memory Cards
- Capacity (SD/SDHC/SDXC/SDUC memory cards)
- SDIO
- ASSD
- Embedded SD
- Application Formats
Simplified Specification Downloads
Simplified versions of selected SD memory card specifications are available for download by developers. To get access to the full specifications, simply join the SD Association.
Start Using SD Standards in Your Products
Interested in using SD standards in your next product?



